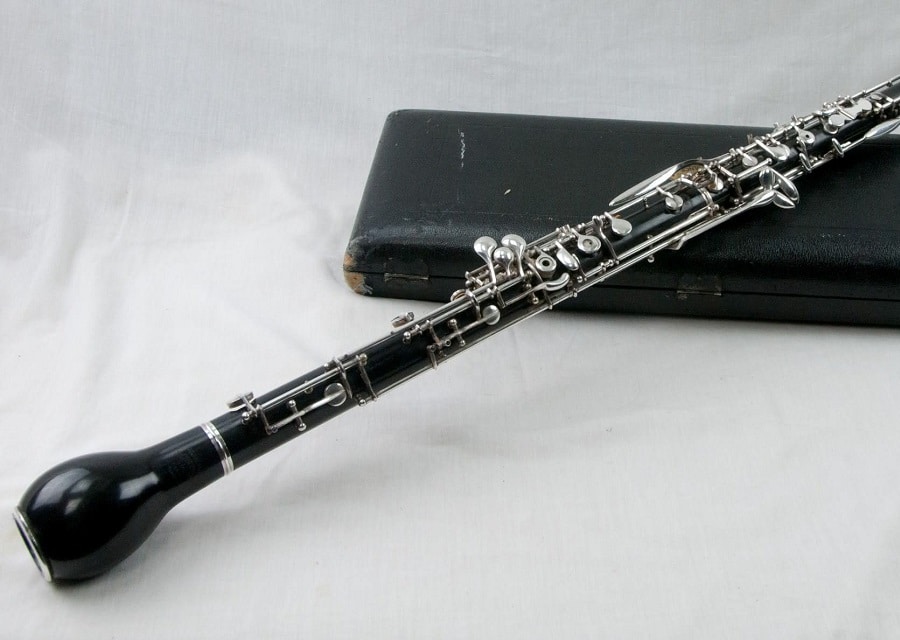
Full size orchestras Trusted Source Orchestra - Wikipedia An orchestra is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. en.wikipedia.org have four main sections and two instruments in the woodwind section are the bassoon and oboe. The woodwind family takes its name because these instruments used to be made fully out of wood. Of course, today, these instruments are made from metal, wood, plastic or a combination of these materials.
Both the bassoon and oboe are firmly in this category and have many similarities. Whether you’re a student deciding between these instruments or you’re simply curious, you will want to know how about the oboe vs bassoon comparison.
In this article, we will explore both the similarities and differences between these two instruments to help you discover which one is the right choice for you.
What is the Oboe?
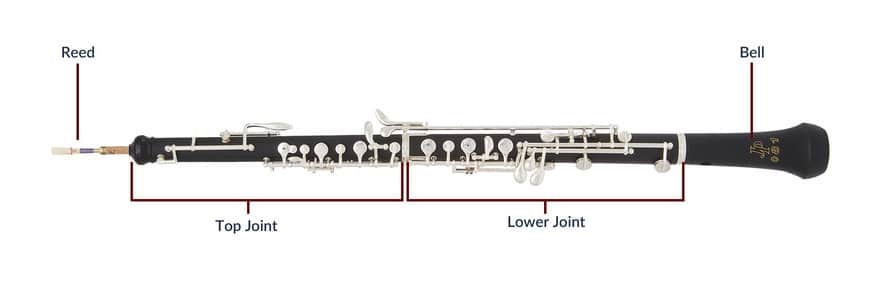
The oboe is a double reed instrument. Beginner oboes typically have a plastic body, but you’re likely to find a grenadilla wood body for more advanced players. Oboe fingering is similar to a recorder, flute, clarinet or saxophone.
The oboe is thought to have been developed in Louis XIV’s court in France in 1657. The instrument evolved, particularly in the 1800s but the final instrument that we are used to today was created in 1906. This model employed finger plates rather than open rings.
The modern oboe has a range of two and a half octaves and this instrument is commonly used to tune an orchestra or band.
What is a Bassoon?

Like an oboe, the bassoon is a double reed instrument that has a distinctive tone and wide range. The bassoon offers a variety of agility and character.
The bassoon dates back from the 16th century, but it was known by a variety of names including the fagot. Originally, it was a single piece of wood with a double reed attached to it.
During the 17th century, this one-piece instrument evolved into a four-piece instrument that managed the massive amount of tubing. However, the bassoon continued to evolve throughout the 18th and 19th centuries.
Bassoon vs oboe: differences
While there are a number of similarities, there are some key differences between the oboe and bassoon.
Size & Appearance
Both the oboe and bassoon have a conical bore, but the long body of the bassoon requires a U turn within its tubing. While the bassoon is almost four and a half feet in length, the oboe is a mere 26 inches. Additionally, while the oboe reed is placed directly into the instrument, the bassoon reed is placed on a bocal.
Range & Sound
The bassoon has a large range that spans over three octaves. This bass clef instrument is in the key of C to create a mellow tone. While the upper octave is tense, the middle octave is light and mellow and the lowest octave has a full tone.
Reeds
While both the bassoon and oboe use a double reed, there are some differences. A double reed has two pieces of can vibrating against each other, but it is placed into the oboe and on a bocal for the bassoon. This is a fine metal tube placed in the instrument.
Reeds for both instruments are sold individually and there are different types available. Store bought reeds are often classified as medium, medium soft or medium hard. This can help players to choose the right reed.
Ease of Learning
You may be interested to know which are the easiest and hardest instruments to play and both the bassoon and oboe are one of the hardest. These instruments take lots of resilience and dedicated practice. So, it is recommended that you find an instructor. This can help guide you through the challenges of learning a double reed instrument.
Both instruments share embouchure challenges, which takes time to solidify. Additionally, tuning is difficult as you can’t simply push in or pull out. Tuning is done by tightening or loosening the embouchure to adjust airflow. You’ll need a good ear, as you’ll need to constantly tune either instrument.

However, since the reed is larger, it is easier to make sounds out of a bassoon. But, if you have smaller hands, you may struggle with fingering and hand positions.
Expert Availability
An expert tutor is invaluable for a developing player as they can teach lessons and share knowledge. Unlike more common instruments such as the clarinet, it is harder to find an expert on the oboe or bassoon. So, you may struggle to find an expert in your local area. Additionally, there are less bassoonists and oboe players required in ensembles, which further reduces experts who are available to teach.
Maintenance
Likewise, maintenance for both these instruments tends to be more complicated. Since the instruments are precise and delicate, you will need someone knowledgeable to correctly adjust them. As with tutors, there are limited maintenance experts. You will need to take your bassoon or oboe to a specialist as they have the knowledge and expertise to ensure the best results.
Since both bassoons and oboes are relatively expensive, it is not a good idea to leave them in the care of someone who doesn’t really know what they are doing. You may get hit with an expensive repair bill if the instrument is not properly cared for. So, don’t assume that your local music shop will have the expertise to adjust your bassoon or oboe.
The Role in Ensemble
Since the bassoon has a mellow tone, it is a superb candidate to blend into many sections. Additionally, its versatility means that it can match trombones and euphoniums while still being able to tackle challenging technical sections with upper woodwinds.
The expressive and colorful tone of the oboe makes it a popular choice for solos. It can be heard easily and has a distinct tone, so it is ideal for lyrical sections. It can be used in challenging upper woodwind sections, but its range can limit use.
Johann Wilhelm Hertel Basson Concerto
Born in Eisenach, a town in Germany, on October 3, 1727, Johann Wilhelm Hertel was a German composer and a great harpsichordist and violinist.
Hertel came from a family of musicians in his hometown. His father, Johann Christian Hertel, was concertmaster of the Eisenach court orchestra and taught him to play the violin and harpsichord.
At age 12, Johann Wilhelm started accompanying his father on concert tours on the harpsichord.
After completing high school, he received violin lessons from the famous violinist Franz Benda and became court music director in Strelitz in 1744 and later in Schwerin (Mecklenburg).
In 1759 to 1760, Hertel was an organist at the St. Mary’s Church, known as Marienkirche, in Stralsund. Later on, he was appointed privy councilor and gave music lessons at the Schwerin court
Compositions
Hertel composed numerous symphonies, solo concertos, piano works, and songs for the courts in Strelitz and Schwerin. He’s credited for the Basson concerto work, “Concerto in a minor (Set of String Parts)-BSN/STGS.”
In later years, he increasingly wrote sacred oratorios and cantatas. Since he wrote music exclusively for the courts in Strelitz and Schwerin, his works were hardly known to the public.
Like his contemporary Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach, Johann Wilhelm Hertel is one of the most important representatives of early German Classicism. His sonatas for harpsichord are in a “sensitive style” typical of the period and can be performed very well on the organ.
Final thoughts
Both the bassoon and oboe are double reed instruments that have an impressive range and distinct sound. While there are some similarities, there are some crucial differences between the two. So, when you’re comparing oboe vs bassoon, you’ll need to think about your playing style and preferences.
Both instruments are challenging to learn. However, while the bassoon is a little easier to play since it is a larger instrument it can be more difficult for those with smaller hands to manage fingering and hand placement.
The oboe has a more distinct sound that makes it more difficult to blend into an ensemble. You will need to practice long and hard to make the best of the instrument as a soloist.
Now you know a little more about the differences and similarities, you can decide which instrument you would prefer to learn or you can distinguish between them when you next see an orchestra.















